Annotation
During the course, students will become familiar with the fundamental principles of 3D computer graphics using the C++ programming language and the OpenGL graphics API (optionally Vulkan), and will gain practical experience with shader programming in GLSL. They will progress through the steps from loading a 3D model to its visualization, including working with cameras, transforming objects and entire scenes, setting up lighting, working with textures, normal maps, shadows, skybox creation, and more.
The deadline for the personal presentation of completed assignments for credit is December 12. The list of tasks for credit corresponds to exercises 3 - 11.
The exam dates are listed in Edison. You must register for the exam in advance.
Lesson plan
| Date | Time | Event |
| 16. 9. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 1 - Vectors, points, basic operations, vector spaces, coordinate systems, transformations, OpenGL template |
| 23. 9. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 2 - Affine space, modeling transformations, initial implementation of the Rasterizer class |
| 30. 9. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 3 - Projective space - camera representation |
| 7. 10. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 4 - Mesh buffers (VAO, VBO, EBO), materials management for fragment shaders (SSBO) |
| 14. 10. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 5 - Implementation of Entity Component System using EnTT library |
| 21. 10. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 6 - Hierarchical transformations using ECS (scene graph), extending materials with textures, practical demonstration of using kinematic character controller (KCC) for handling collisions, slopes, and steps by using sweep tests to move the character and slide it along surfaces |
| 28. 10. 2025 | Free day | |
| 4. 11. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 7 - Normal mapping, TBN space, Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization process |
| 11. 11. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 8 - Instanced rendering - render multiple instances in a single draw call |
| 18. 11. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 9 - Shadow-mapping with shadow-volume calculations and PCF |
| 25. 11. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 10 - Spherical environment map |
| 2. 12. 2025 | 14:15 – 15:45, 16:00 - 17:30 | Lecture and exercise 11 - Procedural snowfall generation using geometry shader |
| 9. 12. 2025 | 14:15 - 17:30 | presentation of the results of tasks assigned during the exercises |
Literature
In addition to the recommended literature listed in the introductory slides of the first lecture, the primary source of information are the lecture notes and accompanying source files.
Credit
The maximum number of points for completing (i.e., implementing and verifying the functionality of) individual tasks can be found here. All submitted assignments are expected to demonstrate perfect familiarity with the source code and understanding of the methods and procedures used. The deadline for obtaining credit is December 12, 2025.
Exam
The exam is oral with written preparation (max. 55 points). The exam questions correspond to the topics covered in the lectures. A list of exam question topics can be found here. The primary source of information for exam preparation are presentations and lecture notes. Additional recommended reading is listed on the slides from the first lecture. Exam dates will be posted during the exam period in Edison.
Lectures
Exercise 1
Introductory exercise mainly explains the representation of geometry, affine and projective spaces, coordinate systems, and affine transformations. The second goal of the first exercise is to get familiar with the template (for VS2022), which can be used to facilitate the completion of tasks from individual exercises. During the exercise, we will discuss the following topics: representation of input geometry (OBJ format), vertices, normals, materials (MTL format), and textures. We will also describe the basic functionality of libraries used to work with the OpenGL API.
Exercise 2
The goal of the second exercise is to create the Rasterizer class based on the tutorials in the template. Class should contain methods for OpenGL context creation, loading OBJ meshes and GLSL shaders, and the main rendering loop.
Exercise 3
In this exercise we should create the camera class allowing as to build view and projection matrices.
Exercise 4
This exercise builds on the previous state of our project by loading meshes into the graphics card memory. We should be able to display the LEGO model using a simple fragment shader (e.g., Lambert or Phong).
Exercise 5
The result of this exercise should be the integration of ECS with the Rasterizer class. ECS will be implemented by the EnTT library.
Exercise 6
During this exercise, we should introduce the hierarchy of transformations of our models loaded into the scene using ECS. You can use the following test models from CGTrader where you can find other free assets. We also discussed options for resolving collisions between player and surrounding objects with an example of using the PhysX library. The result of implementing the topics discussed could look like the image below.
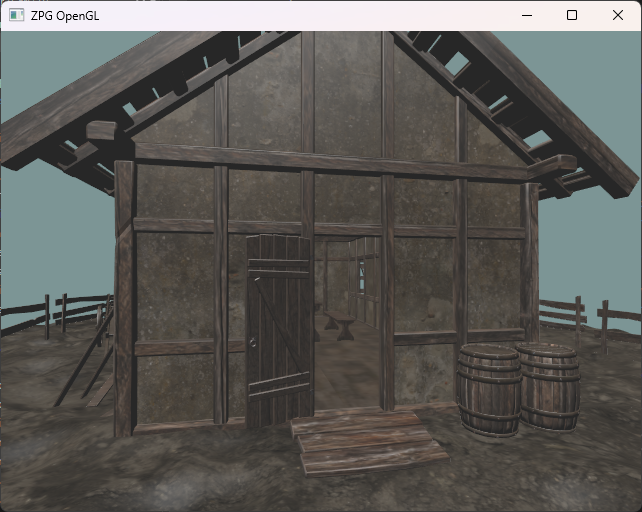
Exercise 7
We add support for normal maps to our rasterizer to enrich the level of detail of surfaces with their natural relief. The result of implementing normal maps could look like the image below.
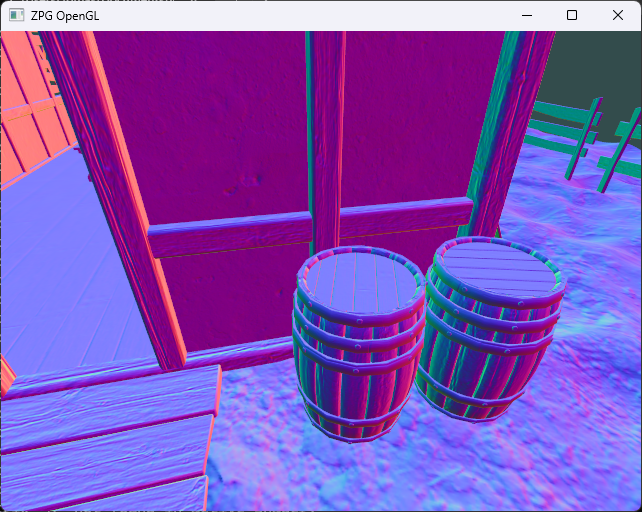
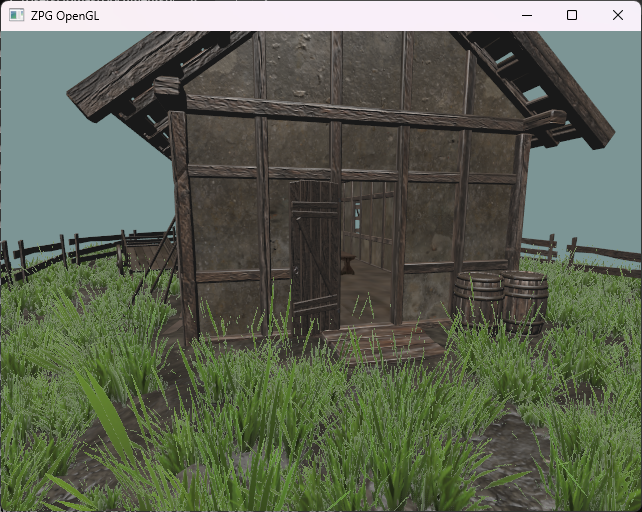
Exercise 8
We added randomly scattered and animated vegetation. The result may look like the image below.
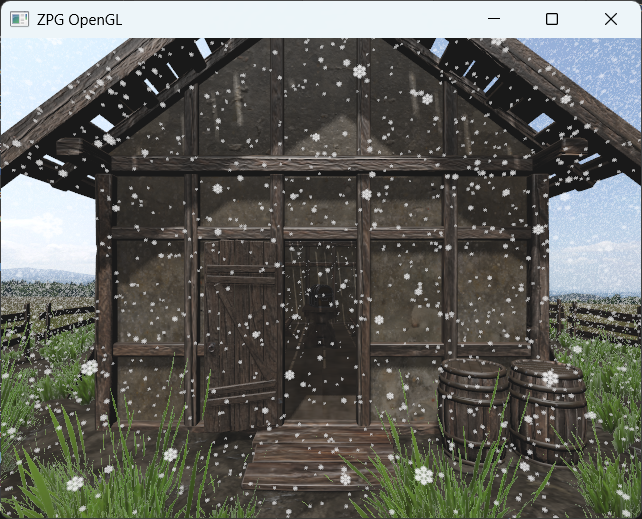
Exercise 9
In this exercise, we implement dynamic shadows by integrating a shadow-mapping pipeline enhanced with shadow-volume calculations. Generate a depth map from the light’s perspective, then use it during scene rendering to determine shadowed fragments. Apply Percentage-Closer Filtering (PCF) to soften shadow edges and improve visual quality. Ensure the solution efficiently handles multiple occluders and produces stable, artifact-free shadows across varying camera and light positions.
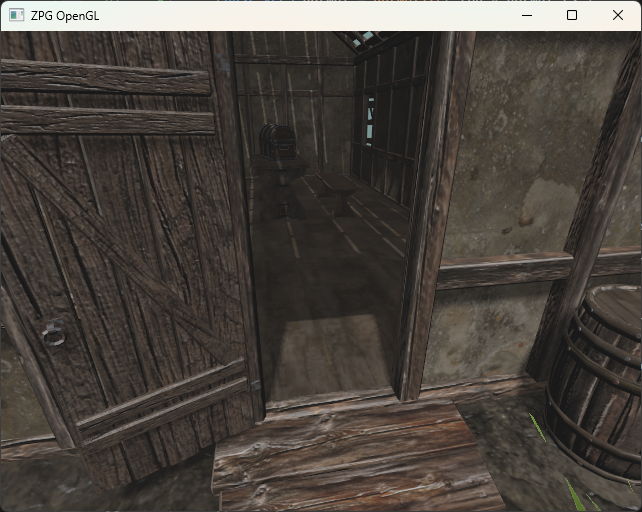
Exercise 10
Here, we integrate a spherical environment map to enhance the visual richness of the scene. The spherical texture will be mapped onto a unit sphere that is projected to infinity in the vertex shader, effectively simulating an environment dome with infinite radius, whose rendering is not affected by changes in camera position, but only by its rotation.
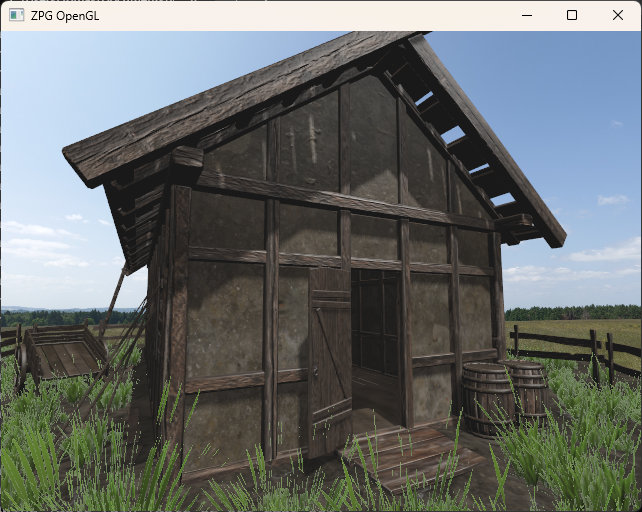
Exercise 11
The goal of the last exercise is to simulate snowfall using a geometry shader. Snowflakes should fall randomly and react to the surrounding geometry, e.g., fewer snowflakes should fall through a leaky roof than in open space. Snowflakes should only be generated within a reasonable distance from the character. This can be achieved, for example, by using a 3x3 grid of tiles defined in the world space and activating them according to the player's current position.